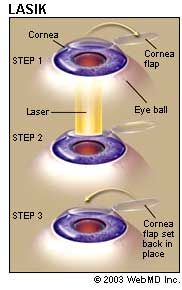
During the LASIK procedure, a specially trained eye surgeon first creates a precise, thin hinged corneal flap using a microkeratome. The surgeon then pulls back the flap to expose the underlying corneal tissue, and then the excimer laser ablates (reshapes) the cornea in a unique pre-specified pattern for each patient. The flap is then gently repositioned onto the underlying cornea without sutures.
What is refractive error?
In the human eye, the front surface (cornea) and lens inside the eye form the eye's "focusing system" and are primarily responsible for focusing incoming light rays onto the surface of the retina, much like the lenses of a camera focus light onto the film. In a perfect optical system, the power of the cornea and lens are perfectly matched with the length of the eye and images are in focus; any mismatch in this system is called a refractive error, and the result is a blurred image at some location.
MYOPIA
A refractive error in which rays of light entering the eye parallel to the optic axis are brought to a focus in front of the RETINA,as a result of the eyeball being too long from front to back.it is called NEARSIGHTEDNESS because the near point is less distant than it is in EMMETROPIA with an equal amplitude of accomodation
People who are nearsighted have what is called a refractive error. This means that the light rays bend incorrectly into the eye to transmit images to the brain. In people with myopia, the eyeball is too long or the cornea has too much curvature, so the light entering the eye is not focused correctly. Light rays of images focus in front of the retina, the light-sensitive part of the eye, rather than directly on the retina, causing blurred vision.
Myopia runs in families and usually appears in childhood. Sometimes the condition plateaus, or sometimes it worsens with age.
What Are the Symptoms of Myopia?
People who are nearsighted often complain of headaches, eyestrain, squinting or fatigue when driving, playing sports, or looking more than a few feet away.
Myopia can be easily diagnosed using standard eye exams given by an eye doctor.
Glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery can correct myopia.
With myopia, your prescription for glasses or contact lens is a negative number, such as -3.00. The higher the number, the stronger your lenses will be.
Refractive surgery can reduce or even eliminate your dependence on glasses or contact lenses. The most common procedures for myopia are performed with a laser, including:
- Photorefractive keratectomy. Also called PRK , a laser is used to remove a layer of corneal tissue, which flattens the cornea and allows light rays to focus closer to or even on the retina.
- Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis. Commonly called LASIK , a laser is used to cut a flap through the top of the cornea, a laser removes some corneal tissue, then the flap is dropped back into place. LASIK is the most common surgery used to correct nearsightedness.
- Corneal rings. Plastic corneal rings, called Intacs, are implanted into the eye to alter the shape of the cornea. One advantage of the rings is that they may be left in place permanently, may be removed in case of a problem, or adjusted should a prescription change be necessary.
